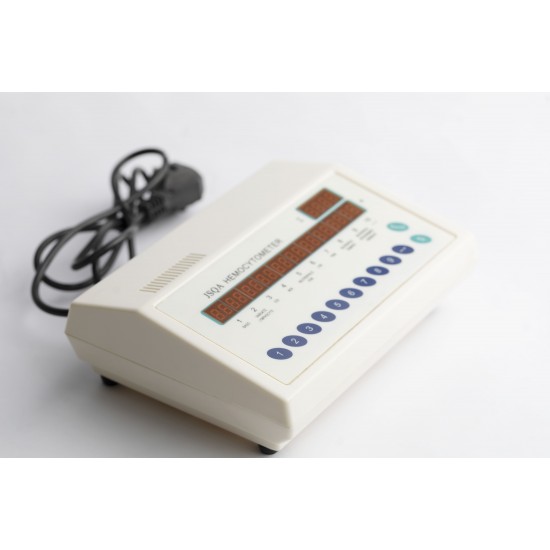
A blood cell counter is a device or tool used in medical laboratories to count and analyze the different types of blood cells in a sample. It is commonly used in hematology to provide insights into a person’s overall health and to diagnose conditions such as anemia, infections, or blood disorders.
Here's what you need to know about blood cell counters:
1. Types of Blood Cell Counters
Manual Blood Cell Counters
- Typically used with a microscope and a hemocytometer.
- Requires a skilled technician to manually count cells.
- Used for smaller sample sizes or when precision in specific cases is required.
Automated Blood Cell Counters
- Found in most modern labs.
- Analyze blood samples quickly and with high accuracy.
- Measure parameters like:
- RBCs (Red Blood Cells): For oxygen transport.
- WBCs (White Blood Cells): For immunity.
- Platelets: For clotting.
- Hemoglobin (Hb): For oxygen-carrying capacity.
2. Parameters Measured
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): The most common test using a blood cell counter.
Includes:- WBC count: High counts may indicate infection; low counts may suggest immune issues.
- RBC count: Abnormal levels may indicate anemia or dehydration.
- Platelet count: Determines clotting ability.
- Hematocrit (HCT): Proportion of red blood cells in the blood.
- Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV): Size of red blood cells.
3. How Automated Blood Cell Counters Work
- Impedance Method: Measures changes in electrical resistance as cells pass through a small aperture.
- Flow Cytometry: Uses lasers to analyze cell size, shape, and granularity.
- Cytochemical Staining: Stains cells to identify different blood cell types.
4. Common Blood Cell Counter Models
Some well-known manufacturers include:
- Sysmex: Produces high-end automated analyzers with advanced technology.
- Beckman Coulter: Offers a range of hematology analyzers.
- Abbott: Known for user-friendly blood counters.
- Horiba: Compact analyzers for small to medium-sized labs.
5. Uses of Blood Cell Counters
- Medical Diagnosis:
Detect conditions like leukemia, infections, or clotting disorders. - Monitoring Therapy:
Evaluate the effectiveness of treatments, e.g., for chemotherapy. - Routine Health Checkups:
Assess overall health and detect abnormalities early.
6. Where to Buy Blood Cell Counters?
- Specialized medical equipment suppliers.
- Online medical stores.
- Ensure the device meets regulatory standards like CE or FDA approval.
If you're looking to get a blood cell counter or related accessories, let me know for further recommendations! ????????











-250x250w.jpg)
-250x250w.jpg)